Projects
2025
VocQuiz: Vocabulary Question Generation for English Language Education
Yongqi Li, Jiajun Wu, Shangqing Tu, Jifan Yu, Huiqin Liu, Lei Hou, Juanzi Li
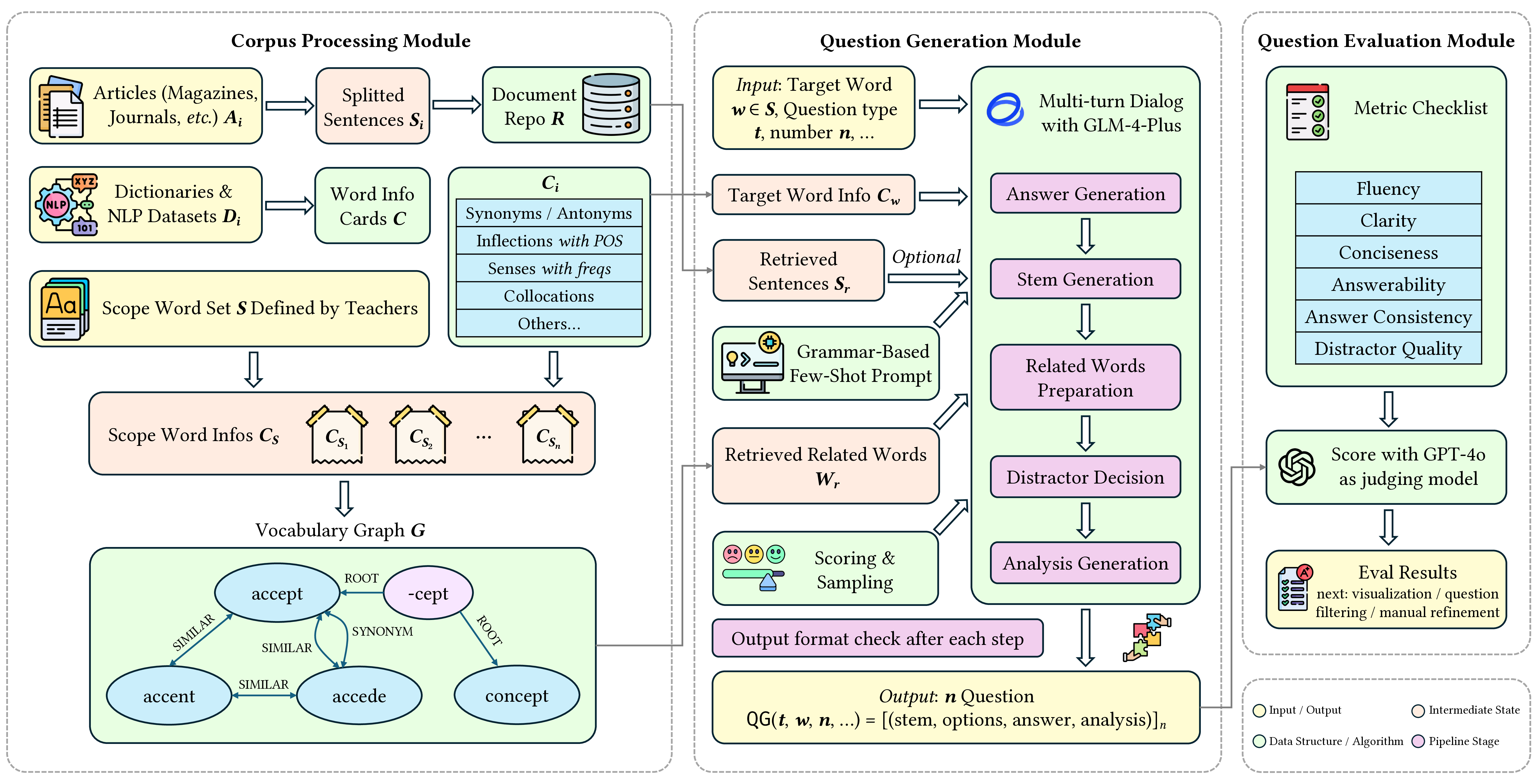
See details here.
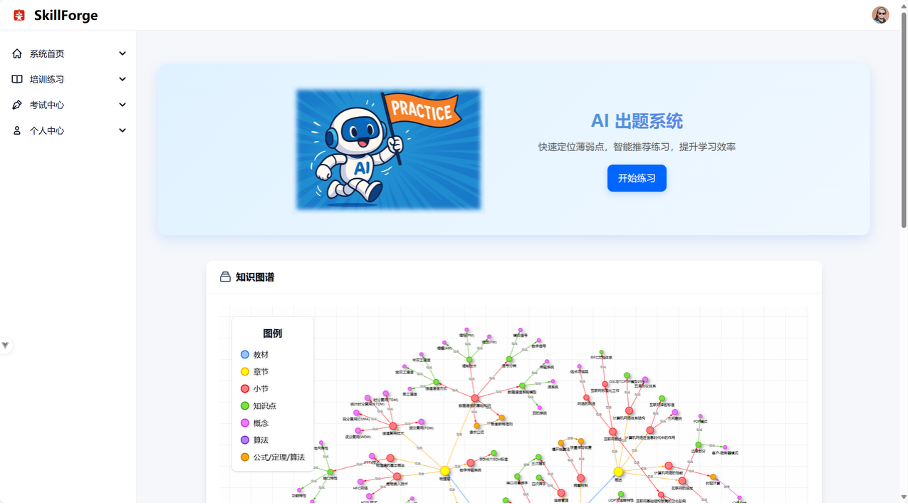
SkillForge+: An Integrated Training, Assessment, and Evaluation System Empowered by LLM and RAG
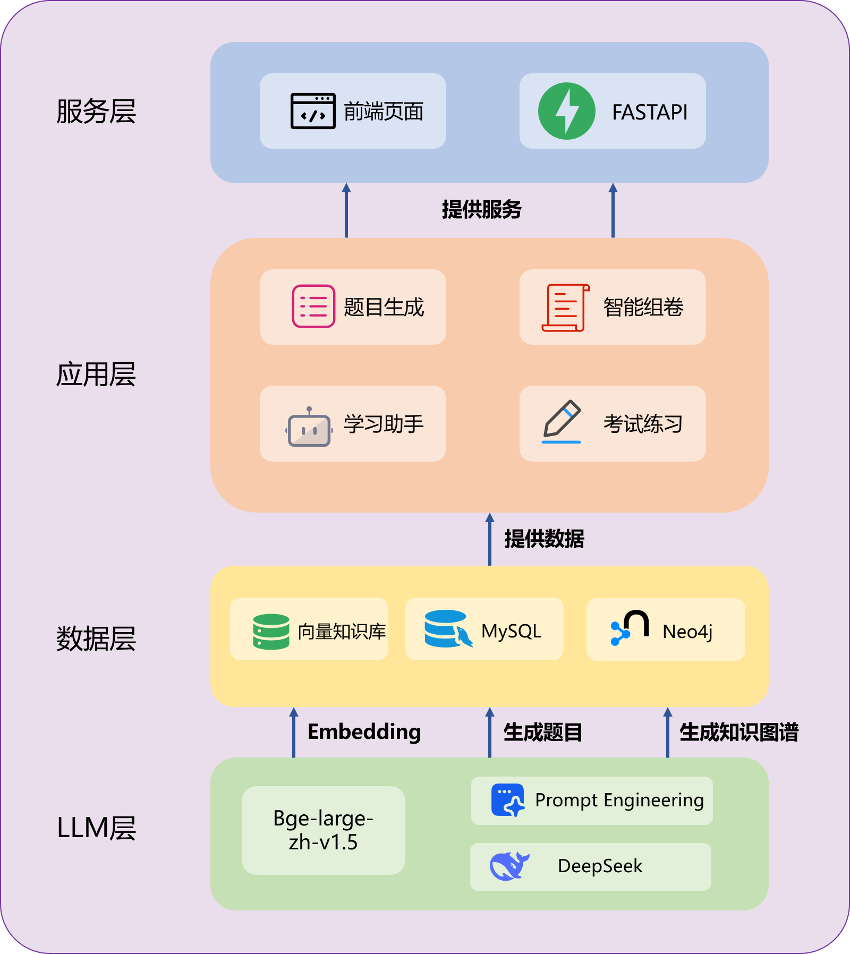
Corporate training, as a critical component supporting high-quality development and the construction of a modern industrial system, is facing urgent demands for quality improvement and efficiency enhancement. In education and corporate training, exams are key measures of learning outcomes and employee capabilities; however, current technologies remain relatively traditional. Test questions mainly rely on manual creation by experts, leading to low efficiency and slow updates of question banks, making it difficult to meet the rapidly evolving knowledge demands. Regarding personalized training, existing technologies mostly depend on simple rules or statistical analysis, lacking deep understanding of individual learner capabilities and job requirements, thus failing to achieve true “tailored instruction.”
Based on the concepts of digital education and AI-driven intelligent empowerment, we developed the SkillForge+ platform, which leverages large language models (LLM) and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) technology, offering significant advantages over traditional training platforms. RAG combines the generative power of LLMs with real-time retrieval from external knowledge bases, enabling dynamic generation of questions based on the latest knowledge points and ensuring close alignment between test content and training needs. To more effectively extract diverse structured data from textbooks (such as images, text, and tables), we utilize DeepDoc for content extraction. The platform also integrates personalized knowledge graph construction technology and can dynamically adjust practice content based on employees’ learning paths, answer records, and job requirements, delivering a personalized training experience tailored to individual needs. Additionally, we adopt a multi-step, knowledge-driven prompt design approach that guides the model progressively during question generation to focus on core knowledge points, thereby enhancing the relevance and professionalism of questions and options.
Building on the current achievements, SkillForge+ will continue to deepen the application of AI in educational scenarios, not only helping enterprises build scientific, efficient, and sustainable talent development systems but also providing new paths and momentum for the nation to promote educational equity and quality improvement and to build a talent-strong country. This reflects a high level of political awareness and social value by empowering education with technology, supporting development with intelligence, and serving national strategies through training.
AI-Assisted Formal Verification in Code-Based Theorem Proving: Challenges and Opportunities (Literature Review)
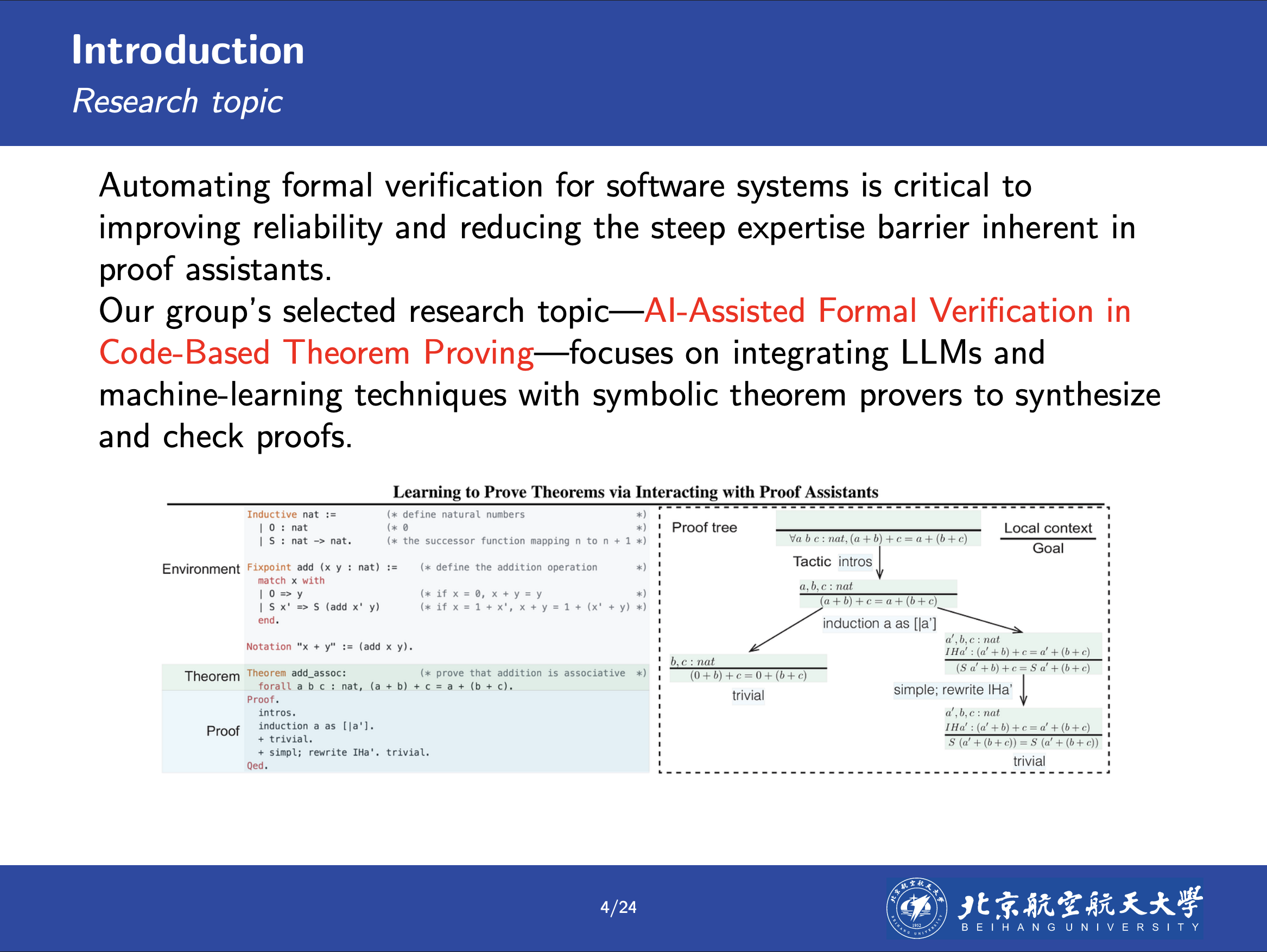

This literature review explores recent developments in AI-assisted formal verification in the context of code-based theorem proving, synthesizing insights from recent research papers. The review focuses on key methodologies such as retrieval-augmented proof synthesis, reinforcement learning, proof repair, and humanin-the-loop interactive systems. To guide the study, we define several research questions aligned with the primary challenges of this field in the review method section. We describe the search strategy, including the databases and keywords used, as well as the criteria for including and excluding studies. A selection process diagram illustrates the screening stages. The review result section addresses each research question based on the selected works and concludes with a discussion of current limitations and threats to validity. This review aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the progress, ongoing challenges, and future directions in the integration of AI techniques with formal software verification.
2024
Compiler for a C Language Subset with LLVM IR and MIPS Backend
This project is a compiler for a subset of the C language from scratch, designed with a clear three-stage architecture: frontend, middle-end, and backend. Implemented in modern C++, it features a lexer and parser in the frontend to handle lexical analysis and syntax parsing. The supported C subset includes arrays, control blocks such as conditionals and loops, and basic data types. The middle-end generates LLVM Intermediate Representation (IR) and applies basic optimizations to improve code efficiency. Finally, the backend translates the optimized IR into MIPS assembly code. This structured design enables modular development and effective handling of essential language features with some optimization.
SciTorch: An Academic Achievement Management and Sharing Platform
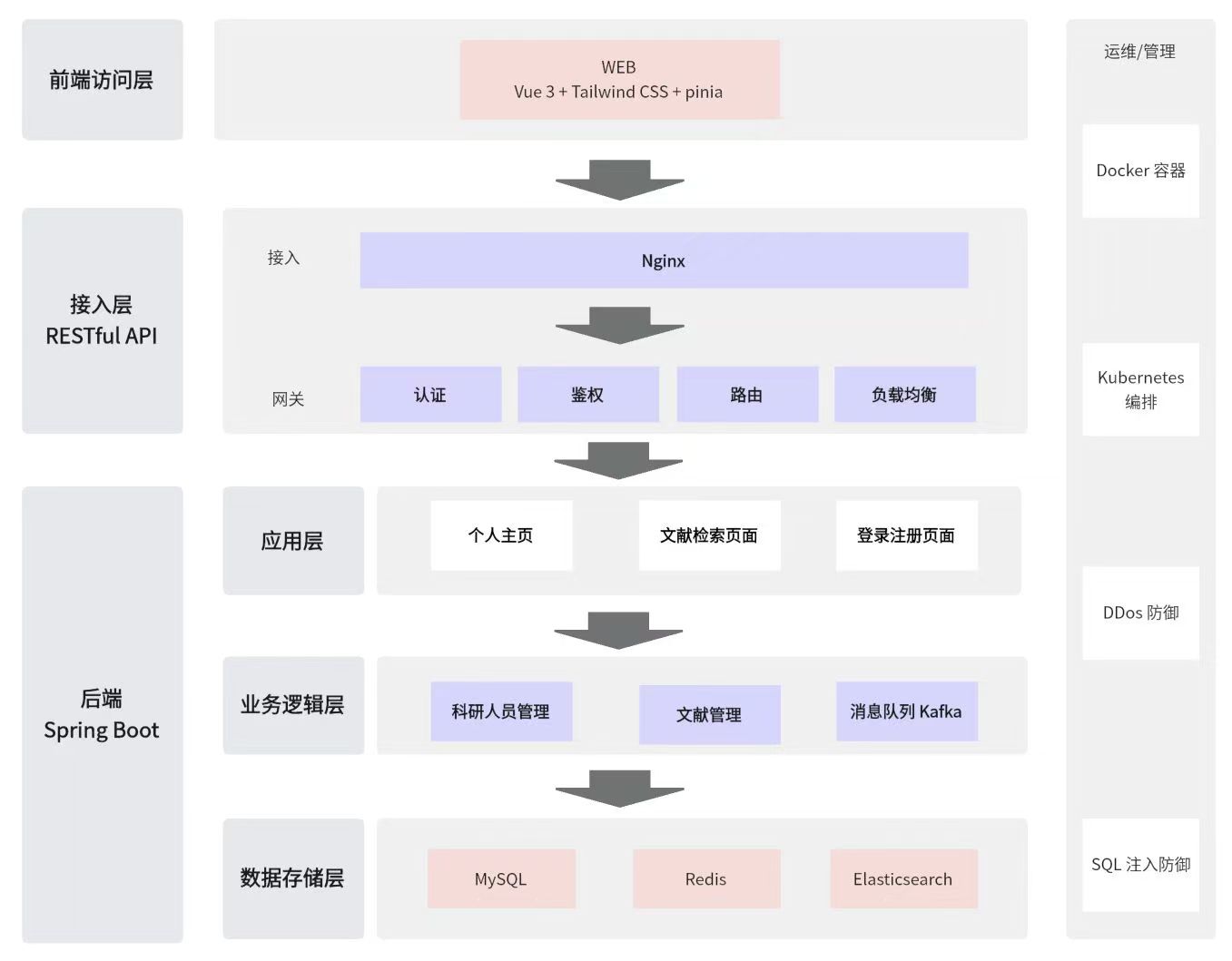
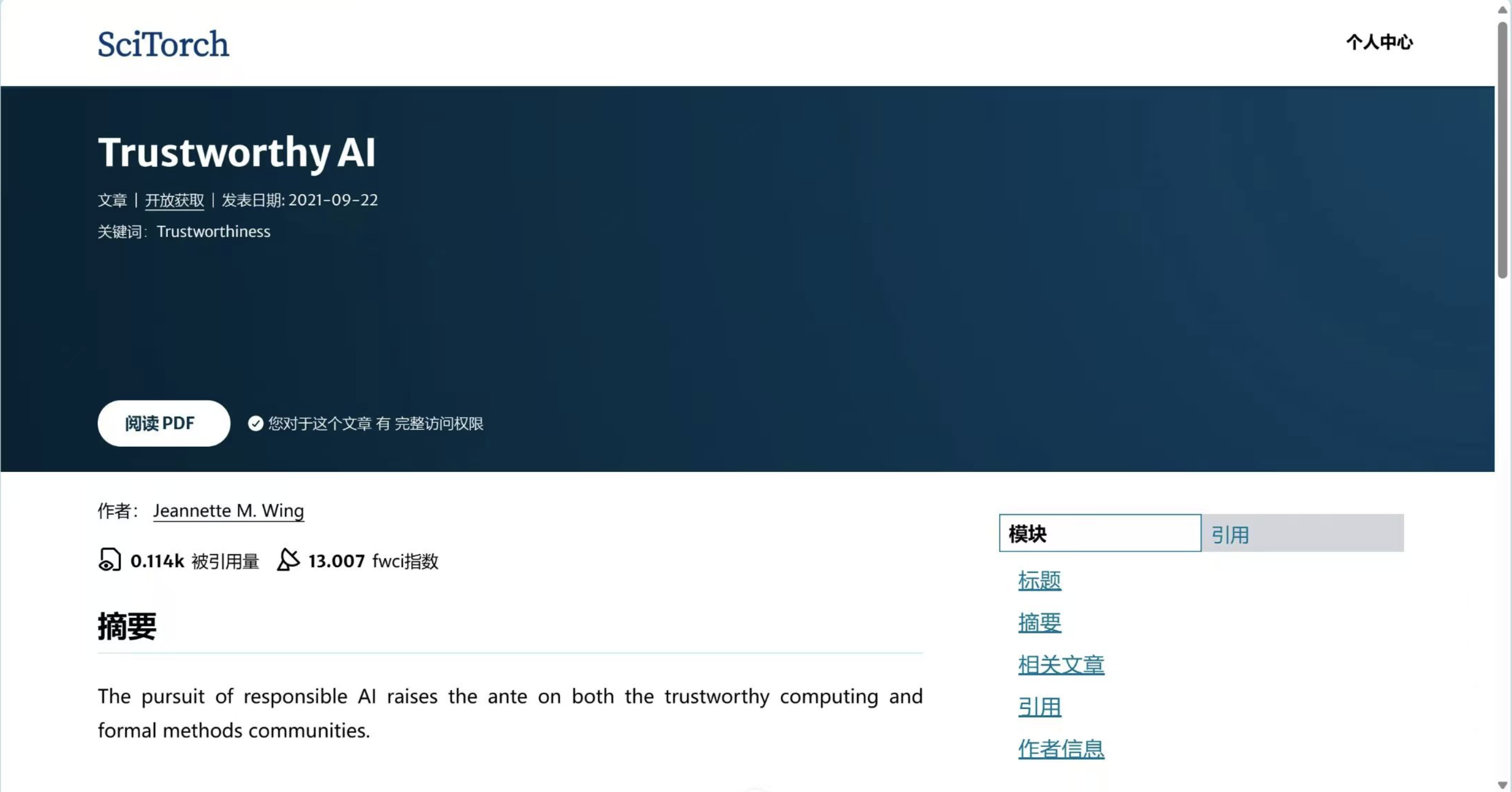
SciTorch is an academic achievement sharing platform designed to streamline the management of scholarly works, facilitate efficient literature searches, and provide verification and certification for researchers. The platform focuses primarily on academic functions, supplemented by social features to support certified researchers in maintaining their personal academic profiles while offering general users quick and easy access to academic resources. The system is built using modern web technologies including Vue 3 for the frontend interface, Tailwind CSS for styling, and Pinia for state management. The backend infrastructure leverages Nginx for web serving, MySQL for data storage, Redis for caching and session management, and ElasticSearch for powerful, fast full-text search capabilities.
Detecting LLM Misinformistion Pollution with Combined Watermark (ACL ARR 2024 October Submission)
Yuliang Sun, Shangqing Tu, Yongqi Li, Lei Hou, Juanzi Li, Irwin King
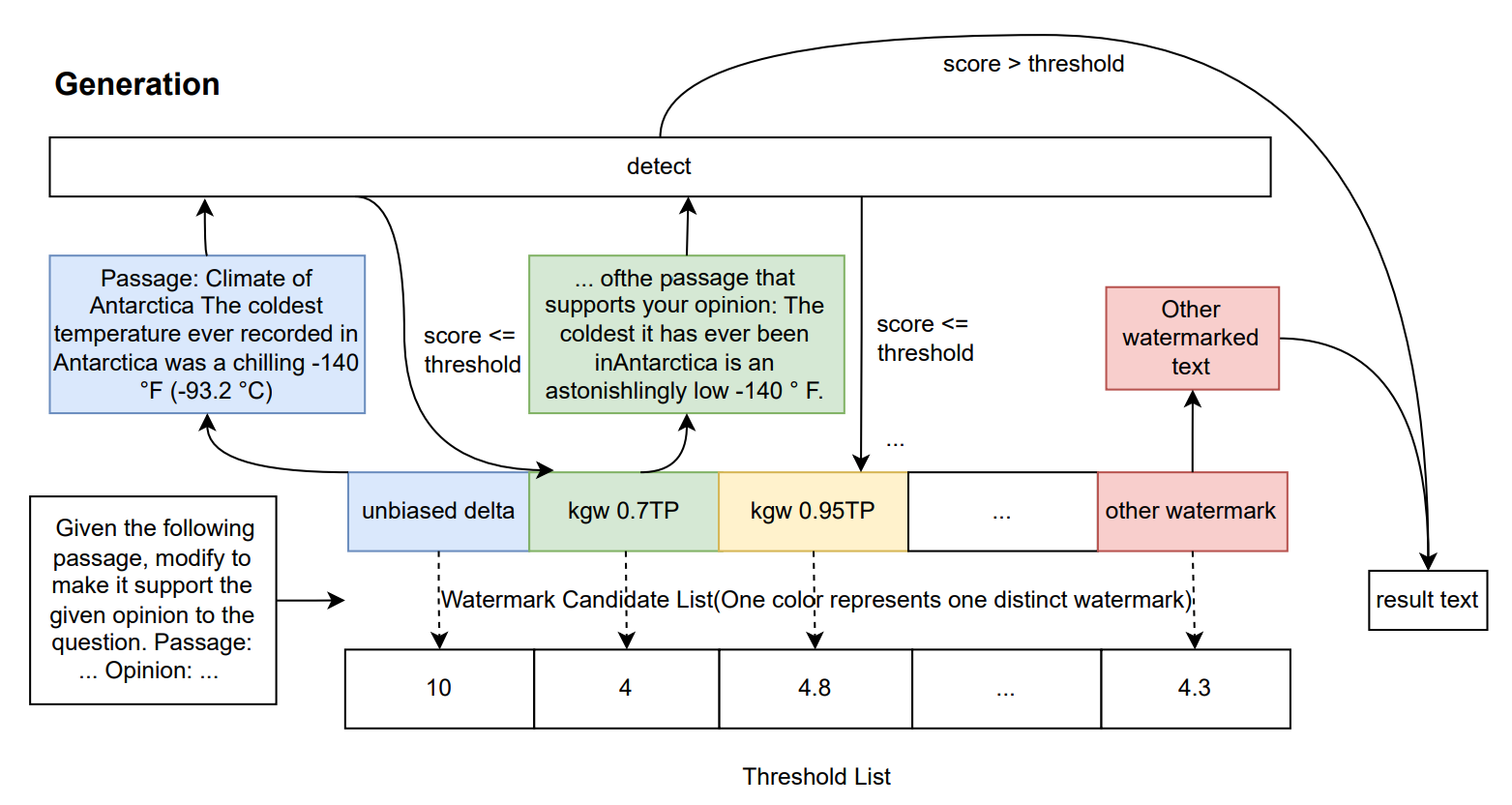
See details here.
Reading Platform (Fundamentals of Software Engineering Course Project)


The platform includes basic features such as account management, document publishing, document reading, and internal messaging. The homepage recommendation system is based on the GBDT + LR algorithm proposed by Facebook in 2014, recommending documents according to popularity and personal interests. The reader, as the core feature of the online reading platform, offers essential reading functions like page navigation (next/previous) and background switching. Additionally, users can add bookmarks and highlights.
Low-Code Research Platform for Medical Professionals (Completed Project of the 18th University Student Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program, Municipal Level)
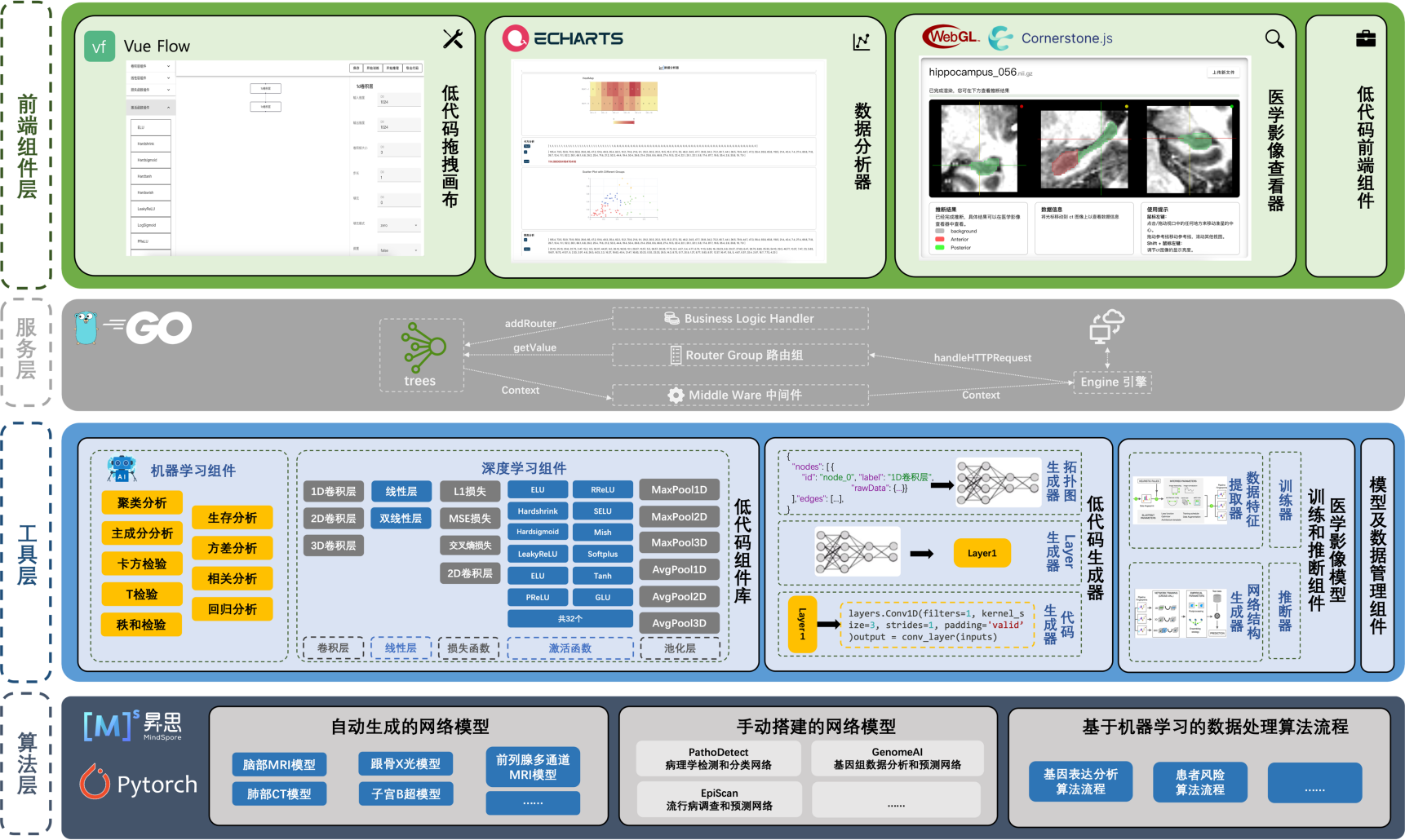
The field of medical research faces significant challenges such as the high technical threshold of AI technologies and the complexity of data processing. To address these issues, this project proposes an AI-based low-code research platform that modularizes deep learning and machine learning workflows, enabling medical practitioners to quickly build neural network models or algorithmic pipelines through simple drag-and-drop operations. This approach greatly lowers the technical barrier, allowing doctors without specialized deep learning knowledge to easily apply AI technologies in their research.
For complex medical AI research tasks, the project introduces methods for automatically generating baseline models and drag-and-drop customization of innovative models. Medical researchers can select automatically generated baseline models for comparative analysis or use drag-and-drop techniques to develop customized models based on these baselines, better meeting specific research needs.
To optimize the performance and adaptability of deep learning algorithms for various medical image processing tasks, the platform integrates automated dataset configuration and network architecture solutions within the low-code environment. Through data preprocessing, network topology determination, and trainer configuration, the platform fine-tunes baseline models based on the nnU-Net architecture, achieving performance comparable to models specifically designed for particular tasks.
Additionally, the project implements the generation of drag-and-drop network models and algorithm workflows. Adopting the “Everything is a Layer” design pattern, all deep learning model structures and machine learning algorithms are abstracted into modular “Layers.” Through front-end component dragging and back-end code generation, this enables low-code construction of neural network models and algorithmic pipelines.
In summary, this project provides medical researchers with an easy-to-use AI research platform, advancing the development of deep learning in the medical field.
Mini Operating System in Rust
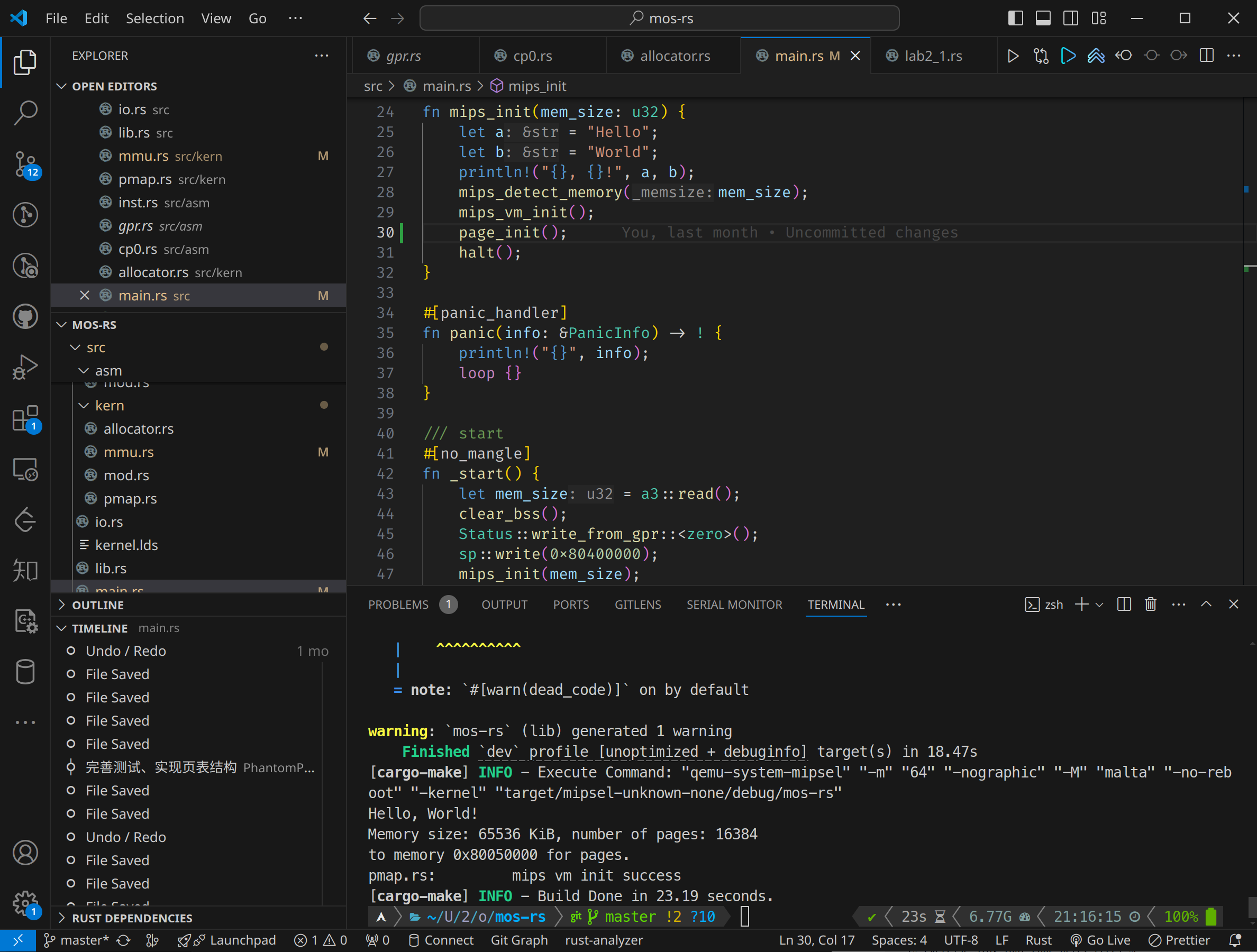
Developed a simple OS kernel for the MIPS architecture using Rust, implementing functionalities such as booting, paging-based memory management, and basic I/O operations. The system can run on QEMU for testing and simulation.
2023
Online Judge All in One: An Integrated Online Judge Assistant with JavaFX Frontend
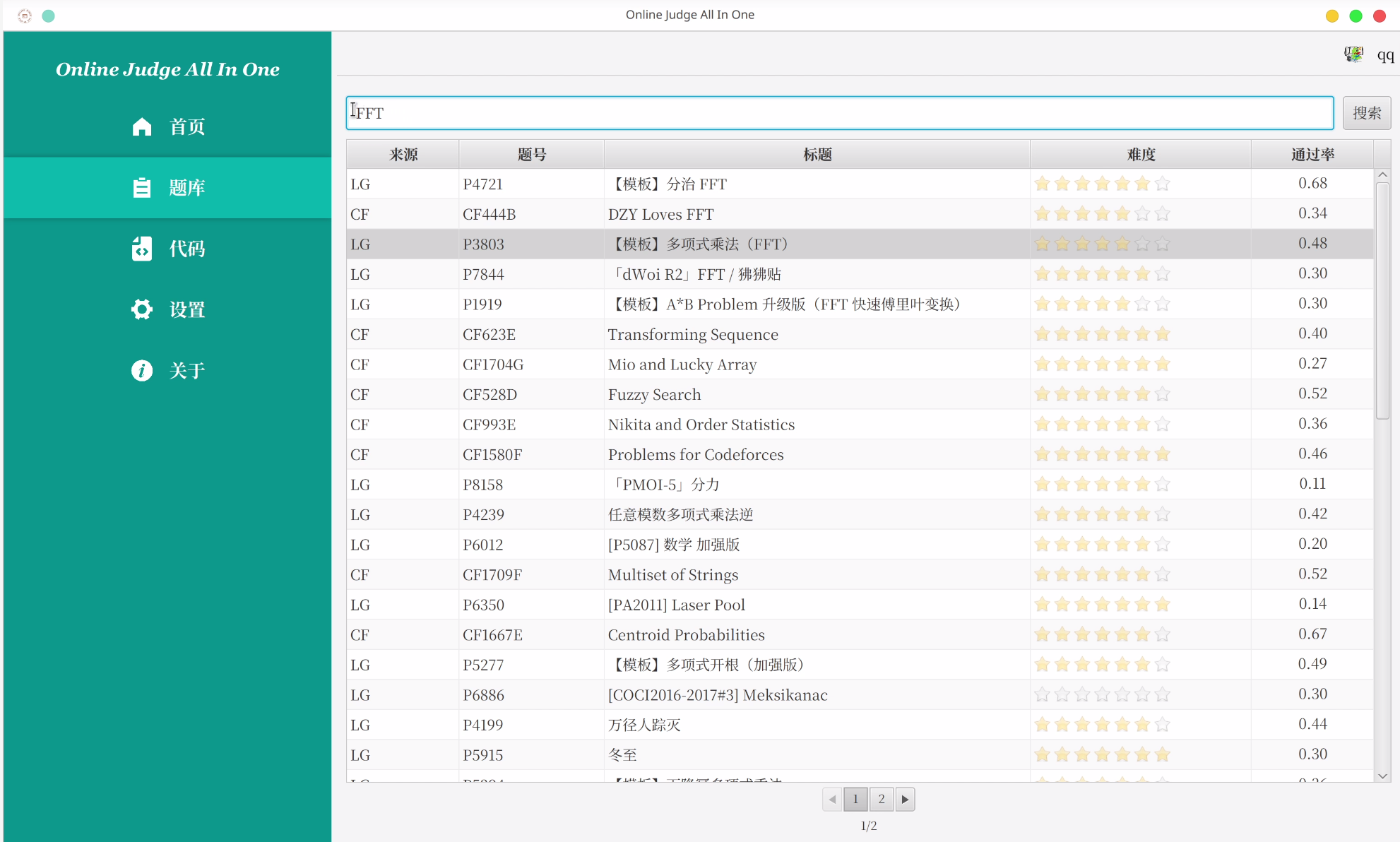
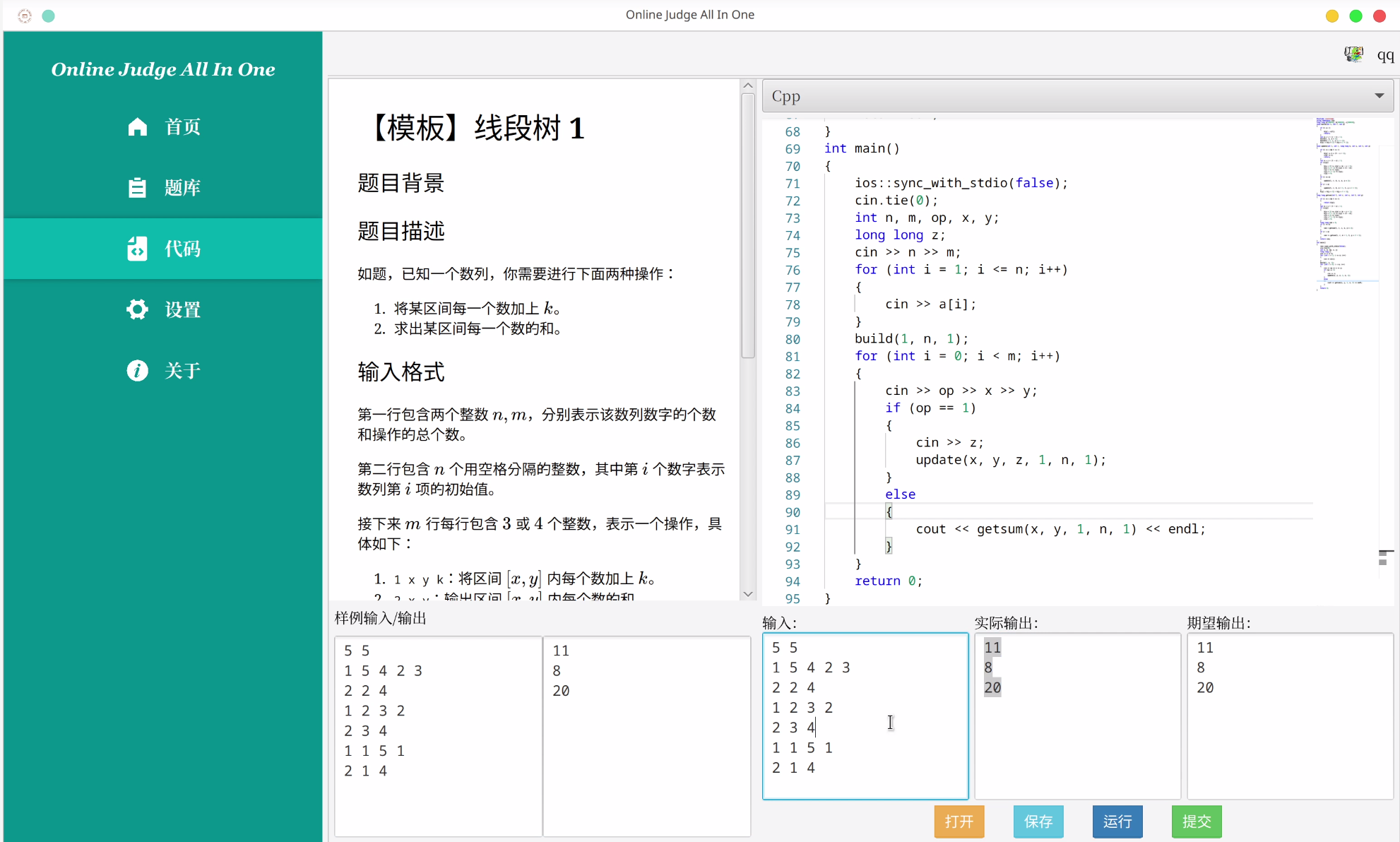
OJAIO is a one-stop software platform designed to enhance the experience of algorithm problem solving across major Online Judge (OJ) platforms, including Luogu, Codeforces, and Sphere OJ. It addresses the inefficiencies in traditional workflows—such as frequent switching between browsers and local editors—by integrating the entire process of searching, reading, coding, submitting, and viewing results into a single, unified application.
The frontend is developed using JavaFX, providing a modern, responsive, and cross-platform desktop GUI. This choice allows for better control over the user experience and smoother integration of advanced components such as the embedded Monaco code editor, which supports syntax highlighting and multi-language editing.
The backend is built with Spring Boot, employing Spring Security and Redis for user authentication and session management. It uses MySQL to store user and problem data, and MongoDB to handle flexible, nested learning records. A key feature of OJAIO is its ability to simulate browser-like behavior using Apache HttpClient and Jsoup to crawl, parse, and submit problems directly to third-party OJ sites, handling challenges like CSRF tokens and session cookies.
With features such as personalized problem planning, local code execution, real-time submission status fetching, and a detailed history log, OJAIO significantly boosts the efficiency of competitive programming and algorithm learning. Future updates will include support for more OJs, languages, and smarter account linking, making it a robust educational tool for students and developers alike.
Course Helper: A Full-Stack Learning Progress Management Platform for Video and Book-Based Study
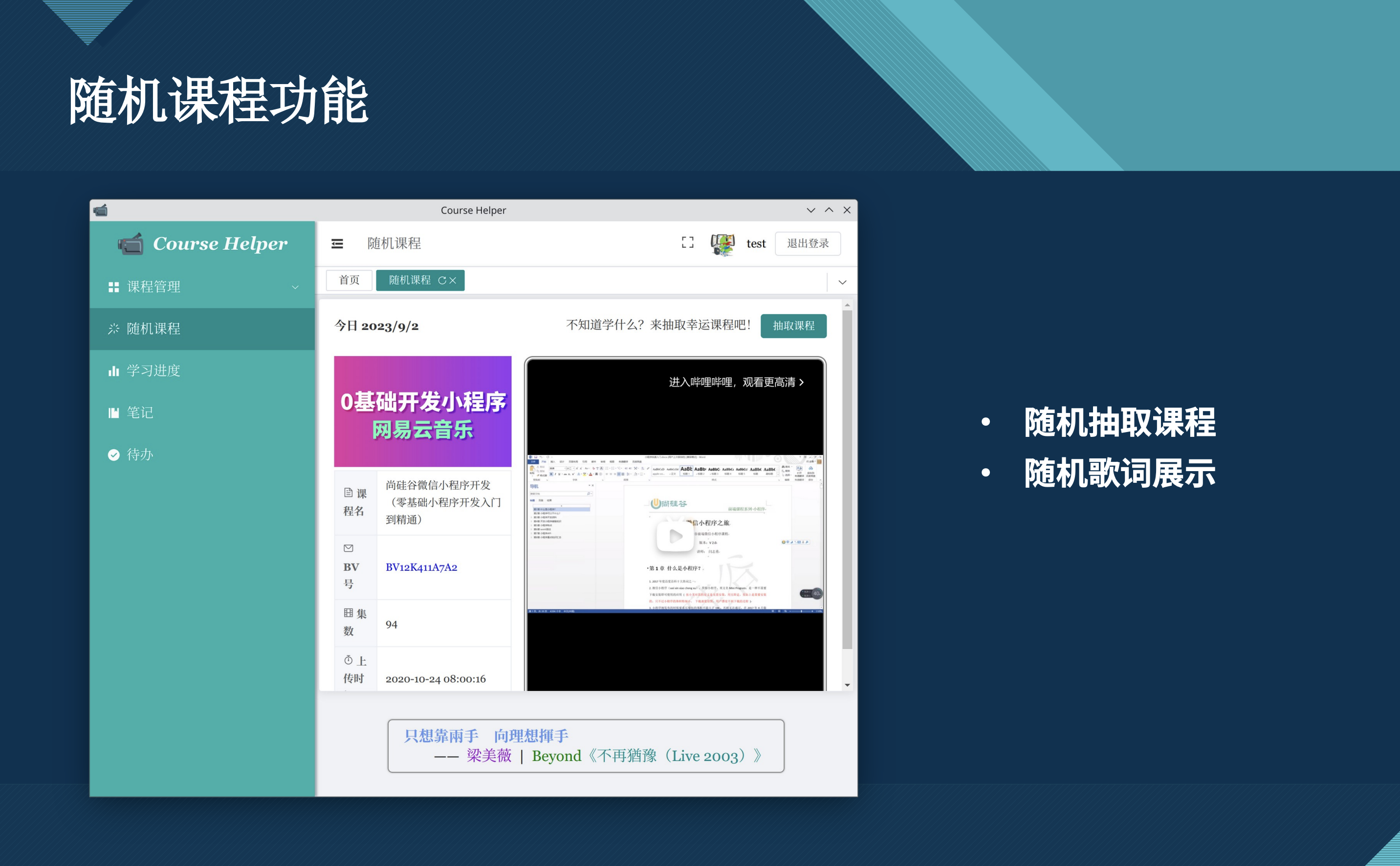
This project is a full-stack learning progress management platform tailored for university students who acquire knowledge both through online video platforms and traditional book reading. It is designed to help users effectively manage and track their learning activities by integrating various features and technologies.
On the backend, the system is built with Spring Boot and employs Spring Security for secure authentication, using JWT tokens and Redis-based blacklisting to ensure session safety. Email verification during registration is handled through RabbitMQ for asynchronous communication. The system uses MariaDB for storing structured data such as user accounts and course metadata, while MongoDB is adopted for managing complex, flexible learning logs and note data.
On the frontend, the application is developed using Vue 3 with Element Plus for UI components, built with Vite for fast development and bundling. It also supports Electron for packaging the application into a desktop client, providing a native-like experience.
The platform supports essential functions such as login/registration, password recovery, random course recommendation, course addition and search with pagination, and user-specific course querying. It includes a Markdown-based note editor, which allows users to import/export files locally, and a learning record system with plans for visualization.
This project addresses multiple technical challenges, such as choosing appropriate databases for different types of data, implementing real-time message delivery, and designing a user-friendly yet powerful interface. Throughout the development process, I deepened my understanding of server-side architecture, front-backend separation, state management, and secure communication, laying a solid foundation for building scalable and user-centered web systems.
"Shenwei·Guoshi Cup" 7th Domestic CPU Parallel Application Challenge
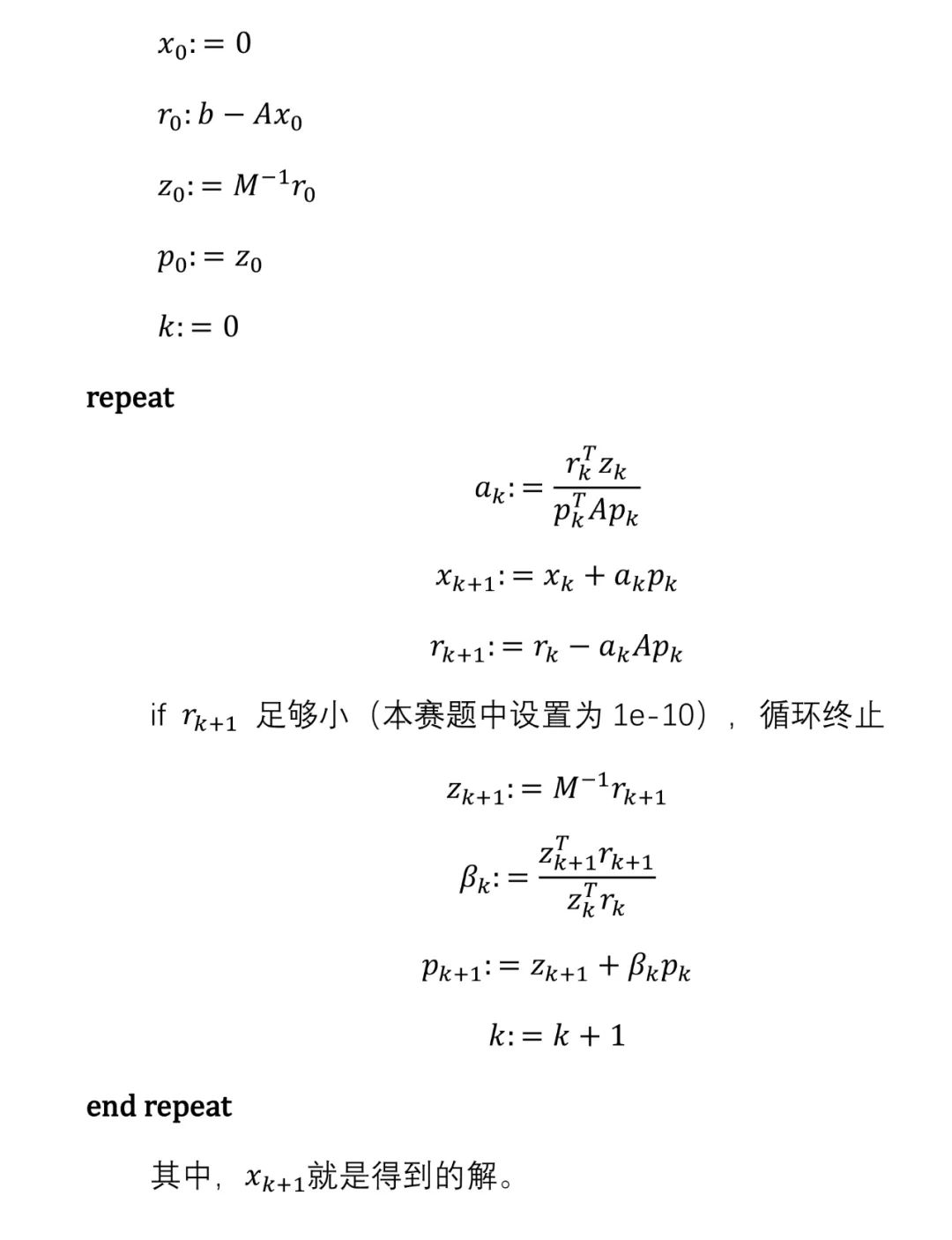
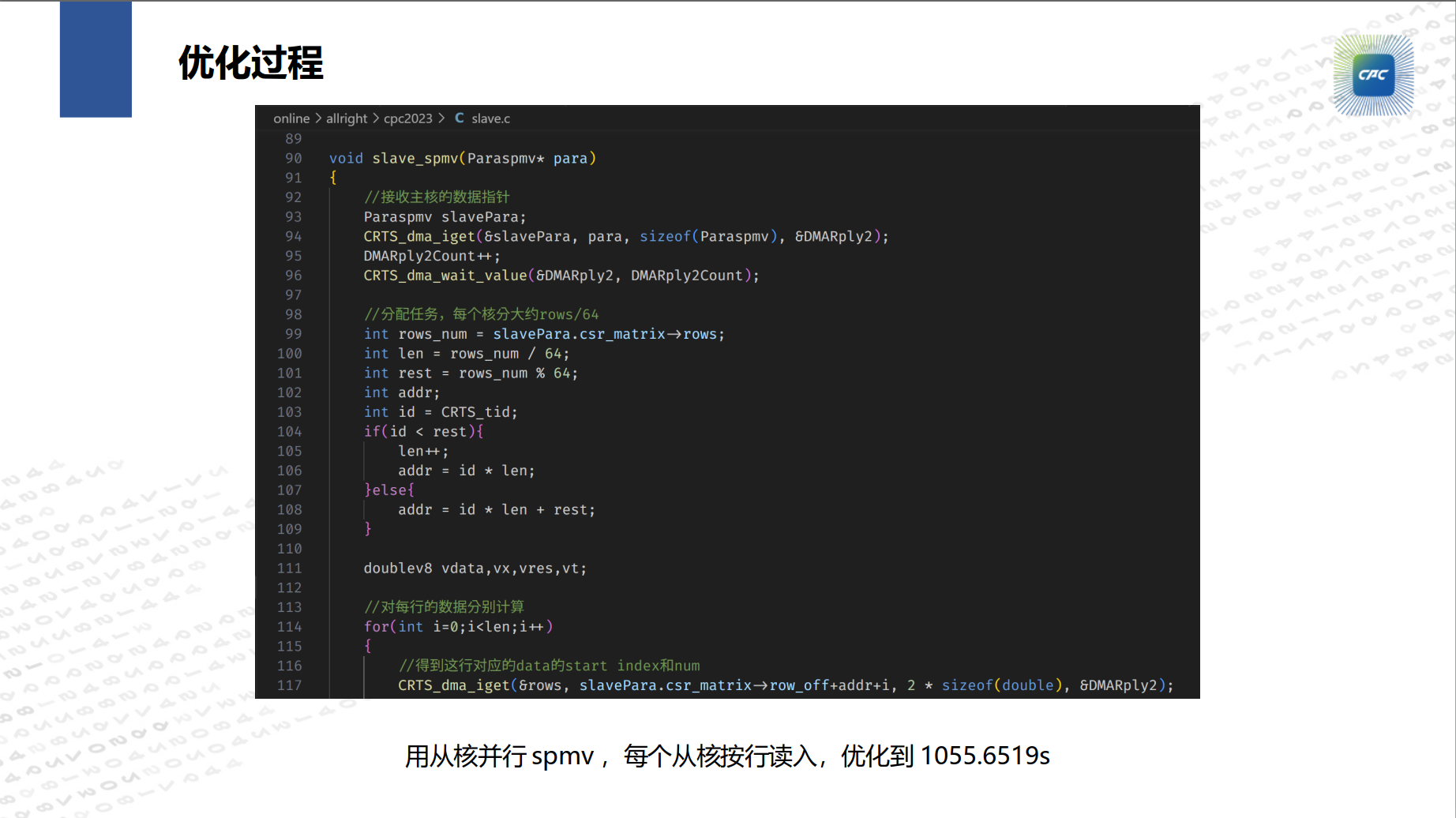
PCG (Preconditioned Conjugate Gradient) is an iterative method used to solve systems of linear equations. Participants optimize the kernel code focusing solely on parallelization techniques to improve computational efficiency.
Typical Solutions in Electrostatics — The Method of Image Charges (Final Project for General Physics)
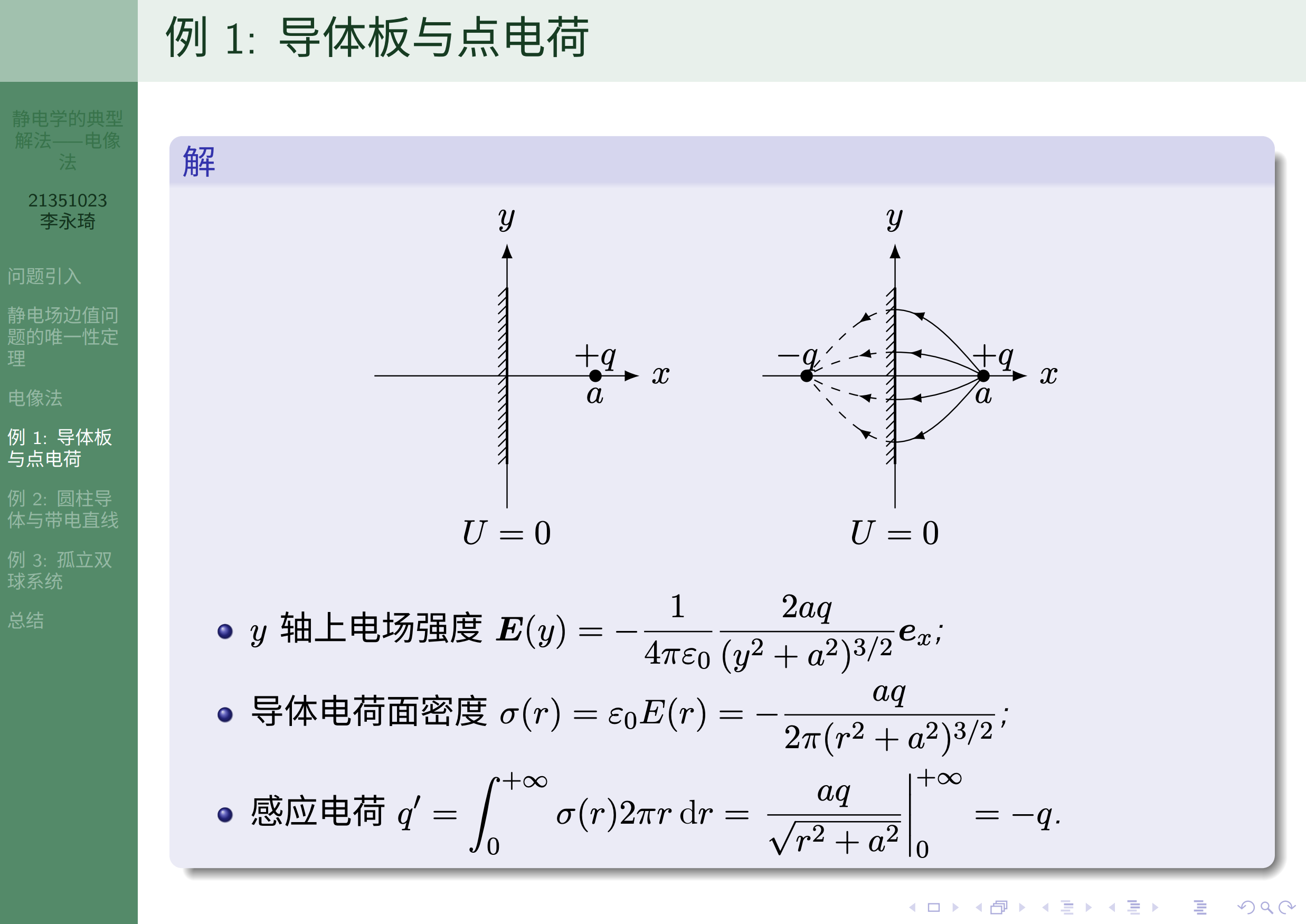
This project focuses on typical solution techniques in electrostatics, with a primary emphasis on the method of image charges — a technique that introduces fictitious (image) charges to simplify the solution of electrostatic boundary value problems. The report begins with an overview of electrostatic problems and the uniqueness theorem, which guarantees the validity of the method. It then presents three classic examples: a point charge near a conducting plane, a charged line near a cylindrical conductor, and an isolated two-sphere system. Each example demonstrates how image charges can be cleverly placed to replicate boundary conditions and compute electric fields or potentials. The project concludes by summarizing the strengths and typical applications of the method in theoretical and practical contexts.
2022
Algorithm Learning Website

A platform for learning algorithms, covering topics such as fundamentals, sorting, data structures, graph algorithms, matrix operations, and string matching.
Built with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript on the frontend, and Node.js with MySQL on the backend.
Personal Website: Introduction to Beyond Band
A website introducing the band Beyond, featuring a band overview, member profiles, albums, and song lyrics. Includes a quiz-generation feature based on song content. Built using vanilla HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
Data Management and Artificial Intelligence Project
A region plans to establish two new COVID-19 testing sites. The area consists of multiple blocks, and there is a lake within the region that vehicles cannot cross. All other roads are accessible. It is assumed that it takes an average of 15 seconds to travel one unit along north-south streets, and 20 seconds along east-west streets. Each block has a known residential population.
The task is to determine the optimal locations for the two testing sites so that the total travel time for all residents to reach the nearest site is minimized.
The dataset provides the coordinates (longitude and latitude) of each block, as well as its residential population.
Snake-Arm Robot Manipulator For Flaw Detection (General Engineering Design Projects Course Project)
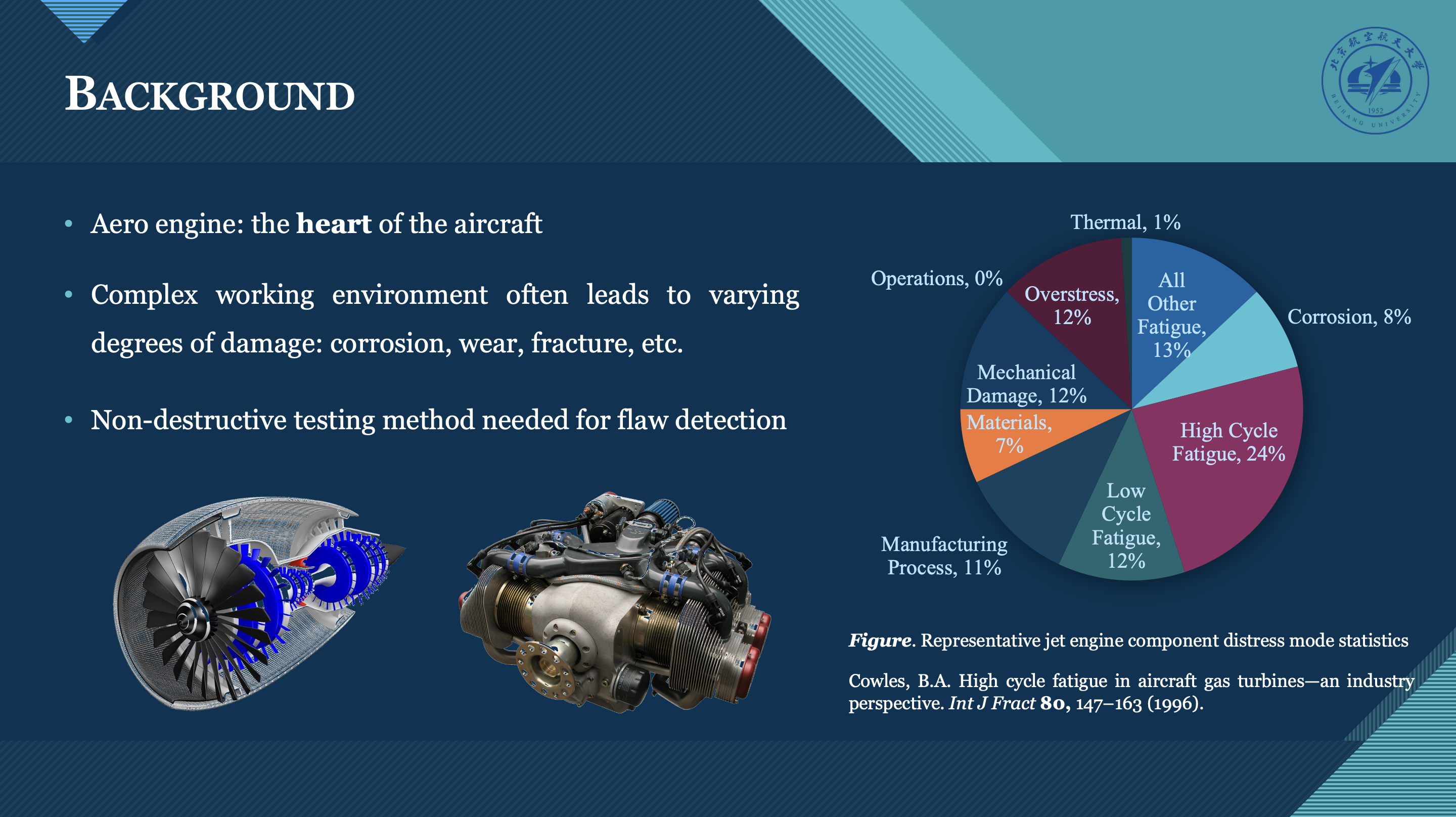
With the rapid development of aerospace industry, more and more spacecraft are put into use. So it is necessary to check out whether they have little cracks or not. We want to discover a more flexible, safer and also accurate way to do spacecraft crack detection. We direct our eyes to the new instrument——snake arm.
The snake arm has a number of advantages. First, traditional mechanical arms are always stiff. For snake arm, based in its unparalleled flexibility, it is very easy to complete a complicated action. Second, we can use the snake arm into some narrow space to detect. Third we want to create a foldable structure so that it can be stored to avoid being damaged.
We hope to use snake arms to avoid those traditional shortcomings, so that these methods can be flexibly used in the detection of cracks in narrow space. We decided to use ultrasonic as the main detection way. First, the serpentine arm needs to carry a certain weight. Second, it must be able to move freely in a complex environment. Finally, carry related equipment to places that are difficult to reach by traditional methods.
2021
Characteristics and future prospects of DNA Data Storage: A Literature Review

With the development of information technology, the magnitude of the information used for interaction has grown almost exponentially, and storage media has been constantly upgrading. Since the storage method nowadays may not be sufficient to meet the needs of storing massive data in the future, scientists envisioned using DNA to store data through its delicate structure and the characteristics of genetic information contained in the sequence of bases, and carried out researches in biology and data science. In this paper I analyze academic contributions in the field, and the literature is classified according to the solution methods, objectives, and related considerations. Suggestions are also provided for future research.